A double-spiral flow channel of vanadium redox flow batteries for
Flow field optimization is an important approach to enhance the performance of vanadium redox flow batteries, with a focus on improving uniform electrolyte distribution while
Get Price
What Are Flow Batteries? A Beginner''s Overview
Part 1. What is the flow battery? A flow battery is a type of rechargeable battery that stores energy in liquid electrolytes, distinguishing itself from conventional batteries, which
Get Price
Comparison of energy losses in a 9kW Vanadium Redox
Among energy storage technologies, vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are receiving increased attention for large-scale applications.
Get Price
Flow Batteries
The main disadvantage of flow batteries is their more complicated system requirements of pumps, sensors, flow and power management, and secondary containment vessels, thus making them
Get Price
Comparison of energy losses in a 9 kW vanadium redox flow battery
An analysis is presented of the losses occurring in a kW-class vanadium redox flow battery due to species crossover, shunt currents, hydraulic pressure drops and pumping,
Get Price
Maximizing Flow Battery Efficiency: The Future of
Flow battery efficiency is a critical factor that determines the viability and economic feasibility of flow battery systems. Higher efficiency
Get Price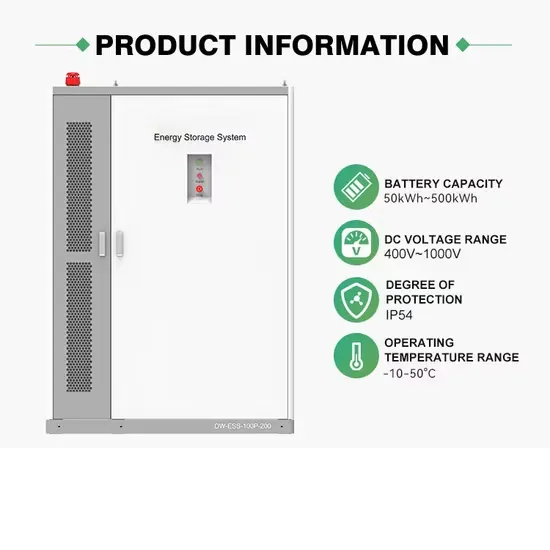
Design trade-offs among shunt current, pumping loss and
Trade-off between shunt current loss and pumping loss is a major challenge in the design of the electrolyte piping network in a flow battery system. It is generally recognized that
Get Price
SECTION 5: FLOW BATTERIES
K. Webb ESE 471 3 Flow Batteries Flow batteries are electrochemical cells, in which the reacting substances are stored in electrolyte solutions external to the battery cell Electrolytes are
Get Price
Mitigation of capacity decay in vanadium redox flow batteries
Abstract Capacity decay due to vanadium cross-over is a key technical challenge for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs). To mitigate this effect this study investigates an
Get Price
Correlations of Through‐Plane Cell Voltage Losses,
Correlations of the through-plane voltage losses in the vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), changes in the posolyte (positive electrolyte) and
Get Price
Optimization of the Shunt Currents and Pressure Losses of a
Using these models, and by using a PSO-type optimization algorithm, specifically designed for discrete variables, the battery design is optimized in order to minimize the round
Get Price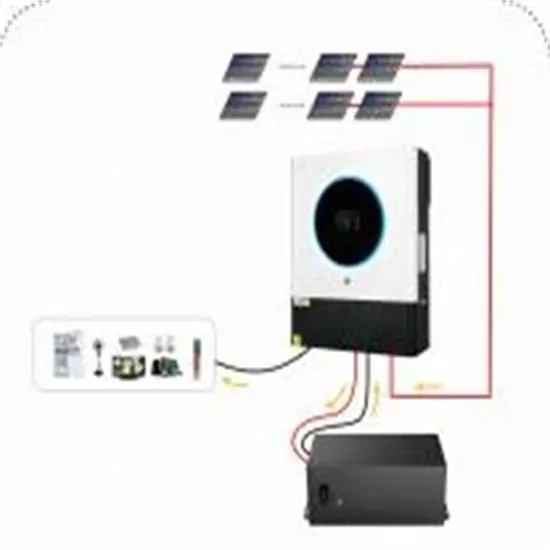
An alternative low-loss stack topology for vanadium redox flow battery
Two vanadium redox flow battery topologies have been compared. In the conventional series stack, bipolar plates connect cells electrically in series a
Get Price
Shunt current analysis of vanadium redox flow battery system
In vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), the electrolyte flowing between cells through channels and manifolds and the electrolyte flowing between stacks through pipes are
Get Price
Comparison of energy losses in a 9kW Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
An analysis is presented of the losses occurring in a kW-class vanadium redox flow battery due to species crossover, shunt current, hydraulic pressure drops and pumping, in
Get Price
Analysis of Concentration Overpotential in an All-Vanadium Redox Flow
This mass transfer resistance thus contributes to voltage losses, referred to as mass transport losses or concentration overpotential, compared to the reversible potential of cell. In
Get Price
Design trade-offs among shunt current, pumping loss and compactness
Abstract Trade-off between shunt current loss and pumping loss is a major challenge in the design of the electrolyte piping network in a flow battery system. It is generally
Get Price
Electrolyte engineering for efficient and stable vanadium redox flow
Taking concentration overpotential and pump losses into account, Tang et al. [190]studied the flow rate effect on battery efficiency (Fig. 10b) in a 40-VRFB cell stack, which
Get Price
Comparison of energy losses in a 9kW Vanadium
An analysis is presented of the losses occurring in a kW-class vanadium redox flow battery due to species crossover, shunt current,
Get Price
Study on the Influence of the Flow Factor on the Performance of
One factor that critically affects battery efficiency is the flow rate. The flow rate is related to the charge or discharge current of the battery and the electrolyte flow rate. It also
Get Price
A complex four-point method for the evaluation of ohmic and
We propose a complex 4-point method for characterization of flow batteries. The distribution of ohmic and faradaic losses within a single-cell is evaluated from electrochemical
Get Price
Flow batteries for grid-scale energy storage
A promising technology for performing that task is the flow battery, an electrochemical device that can store hundreds of megawatt-hours of
Get Price
A comparative investigation on the energy flow of pure battery
Sun et al. [41] tested the energy flow of EVs under WLTC and CLTC conditions, focusing on the impact of temperature on the power battery and motor. The energy flow
Get Price
Vanadium redox flow battery capacity loss mitigation strategy
Electrolyte imbalance is the main cause of capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries. It has been widely reported that imbalance caused by vanadi
Get Price
A response time-based method to operando decouple the
The polarization of redox flow batteries (RFBs) consists of activation polarization, ohmic polarization, and concentration polarization. However, the three types of polarizations
Get Price
Studies on pressure losses and flow rate optimization in
In this paper, the concentration overpotential is modelled as a function of flow rate in an effort to determine an appropriate variable flow rate that can yield high system efficiency,
Get Price
Maximizing Flow Battery Efficiency: The Future of Energy Storage
Flow battery efficiency is a critical factor that determines the viability and economic feasibility of flow battery systems. Higher efficiency means more of the stored energy can be
Get Price
Correlations of Through‐Plane Cell Voltage Losses, Imbalance of
Correlations of the through-plane voltage losses in the vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), changes in the posolyte (positive electrolyte) and negolyte (negative electrolyte)
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Flow Battery Losses]
How does flow factor affect battery efficiency?
Linking with Eq. 22, the higher the current, the greater the flow rate needed; therefore, the pressure losses will increase, implying a higher need for pump power. This probably directly limits the value of the flow factor. Knowing the optimum flow factor for battery operation is of great interest to optimize battery efficiency.
How do flow batteries work?
K. Webb ESE 471 3 Flow Batteries Flow batteries are electrochemical cells, in which the reacting substances are stored in electrolyte solutions external to the battery cell Electrolytes are pumped through the cells Electrolytes flow across the electrodes Reactions occur atthe electrodes Electrodes do not undergo a physical change Source: EPRI
What are the disadvantages of flow batteries?
The main disadvantage of flow batteries is their more complicated system requirements of pumps, sensors, flow and power management, and secondary containment vessels, thus making them more suitable for large-scale storage applications. current vanadium prices, or from 50 to 100 percent of the aforementioned cost target of $100-200/kWh.
Should pump losses be considered in battery design and operation?
Therefore, pump losses need to be considered in battery design and operation in addition to any shunt current losses. Fig. 2. Stack voltage curves at current density of 75 mA cm −2 and different constant flow rates (experimental data adapted from Ref. ).
What factors affect battery efficiency?
In addition, a PSO type technique is introduced to optimize the battery design. Neither study considers activation and concentration overpotentials. One factor that critically affects battery efficiency is the flow rate. The flow rate is related to the charge or discharge current of the battery and the electrolyte flow rate.
Do flow batteries need a fluid model?
Flow batteries require electrolyte to be pumped through the cell stack Pumps require power Pump power affects efficiency Need a fluid model for the battery in order to understand how mechanical losses affect efficiency K. Webb ESE 471 29 RFB Fluid Model Power required to pump electrolyte through cell stack Pumping power is proportional to
More related information
-
 Austria Flow Battery Wholesale
Austria Flow Battery Wholesale
-
 Solar Base Station Flow Battery Construction Plan
Solar Base Station Flow Battery Construction Plan
-
 Organic flow battery manufacturers
Organic flow battery manufacturers
-
 Nickel-chromium flow battery
Nickel-chromium flow battery
-
 Flow Battery Professional
Flow Battery Professional
-
 Flow battery device purchase
Flow battery device purchase
-
 Qatar communication base station flow battery station planning requirements
Qatar communication base station flow battery station planning requirements
-
 Zinc-based flow battery energy storage
Zinc-based flow battery energy storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
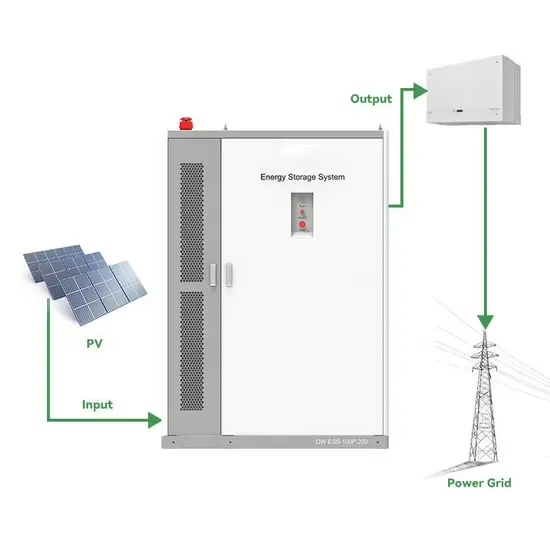
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


