How to Troubleshoot Motors and Drives at the Inputs
Here we look closely at the first segment in a typical three-phase motor and drive system: from the mains supply at the drive input to the drive itself,
Get Price
Motor Inverter vs VFD: What''s the Real Difference? | Mingch
A motor inverter and a variable frequency drive (VFD) are related, but not identical. The term motor inverter often refers to the DC-to-AC conversion stage that powers a motor. At
Get Price
MOVIDRIVE® Drive Inverters / Brochures / 2006-04
Whether controlling asynchronous AC drives or synchronous servo drives, MOVIDRIVE® drive system can be extended at any time as application requirements change. inverters provide
Get Price
Discover the Power Behind Your Devices: How Do Inverters
Verify the inverter''s surge capacity to handle startup spikes, especially for motors or compressors. Understanding how do inverters how do they work in harmony with your device
Get Price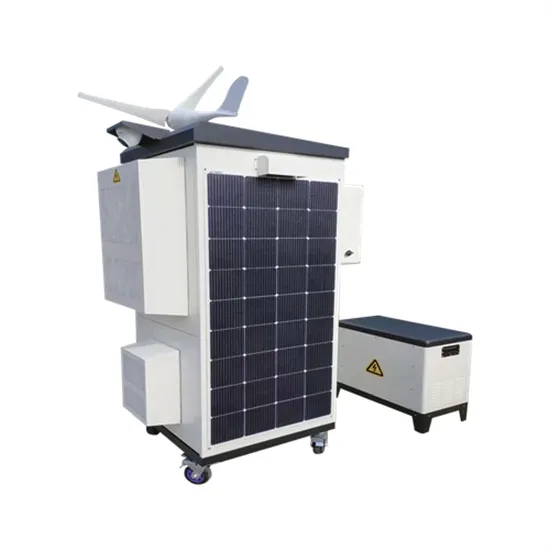
What''s the Difference Between a Motor Drive and an Inverter?
At a high level, an inverter converts DC to AC. That''s its sole function — power conversion. A motor drive, on the other hand, builds on that by using an inverter to actually
Get Price
The 3 Most Common Faults on Inverters and how to
At IDS we have a wealth of inverter experience. We have been an ABB Partner for over 20 years and are used to supporting clients with a variety of inverter
Get Price
Difference between motor inverter vs motor controller – TYCORUN
This article will focus on four aspects to introduce motor inverter: the role of motor inverter, the difference between electric motor inverter and motor controller, the cause of motor
Get Price
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to operate a motor. Inverters also introduce
Get Price
What is an Inverter Drive and what are its features?
An inverter drive, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD) or adjustable frequency drive (AFD), Darwin Motion Micro Drive- Matrix 900, DR Matrix 350 / Solar Drive,
Get Price
A Guide to Inverter Drives | RS
Inverter drives are essential for applications requiring variable speed motors, such as industrial automation and HVAC systems. They convert fixed frequency AC power from the
Get Price
How an Inverter Drive Works and Controls the Speed of an AC Induction Motor
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get Price
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types, Uses, and
Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect choice.
Get Price
AC Motor Drives Selection Guide: Types, Features,
AC motor drives are defined as amplifiers or frequency inverters that interface between a controller and an AC motor. They convert step and direction input
Get Price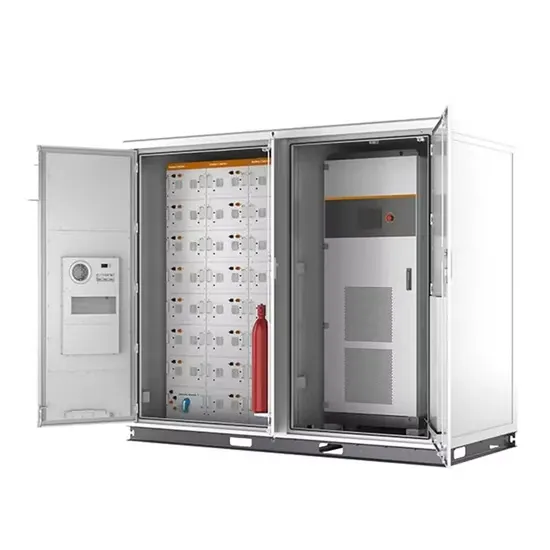
Difference between motor inverter vs motor controller
This article will focus on four aspects to introduce motor inverter: the role of motor inverter, the difference between electric motor inverter and
Get Price
Variable Frequency Drive & AC Motor Drive Inverter
An inverter drive is a type of electrical control system used in electro-mechanical motive power systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor
Get Price
Motor-drive systems
2.1 - Recapitulation of the principle of operation of electronic drives An electronic drive, otherwise known as a frequency inverter, provides power supply to an electric motor at variable voltage
Get Price
How an Inverter Drive Works and Controls the Speed of an AC
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get Price
The Secret Behind Electric Motors: Inverter Explained
In this video, we break down how a motor inverter works and why it''s a critical component in electric vehicles (EVs) and modern motor systems.
Get Price
Matching motors and drives: Common problems and
While it''s common to use the same manufacturer for a motor or drive, when something breaks down, the choice might not be so
Get Price
Understanding the Distinction Between AC Drives and Inverters
Discover the nuanced disparity between AC drives and inverters. CM Industry Supply Automation (Lenze Drive & Keb Drive Supplier) Unravel their unique functionalities and
Get Price
Understanding Electronic Motor Drives
A motor drive controls the speed, torque, direction, and resulting horsepower of a motor. Dc drives typically control a shunt-wound dc motor, which has separate armature and
Get Price
A Guide to Inverter Drives | RS
Inverter drives are essential for applications requiring variable speed motors, such as industrial automation and HVAC systems. They
Get Price
Understanding the Distinction Between AC Drives and Inverters
While AC drives are a type of inverter, not all inverters serve the function of motor speed control. In the context of motor control, inverters typically refer to devices that convert
Get Price
What''s the Difference Between a Motor Drive and an
At a high level, an inverter converts DC to AC. That''s its sole function — power conversion. A motor drive, on the other hand, builds on that
Get Price
What is an
Power then flows from a capacitor to an inverter which changes the DC power to the output AC power that goes to the motor. This step allows the drive to adjust the frequency and voltage
Get Price
AC Motor Inverters: How They Work, Principles, And Technical
Enhanced energy efficiency occurs when AC motor inverters optimize the power delivered to the motor. Inverters adjust the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor based
Get Price
Electric Motor Inverter Explained
EV inverters do more than drive the motor — they also enable regenerative braking by reversing the power flow: Instead of pushing current to the motor, the inverter
Get Price
How to Use a Frequency Inverter? | inverter
The frequency inverter can be used without an incoming contactor. The incoming contactor can be used for stopping operation, but then the
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Whether the motor drives the inverter power]
How do inverter drives work?
Inverter drives, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or frequency inverters, are electronic devices used to control the speed and torque of three phase electric motors. They achieve this by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control over motor speed.
What is an inverter motor?
An inverter motor, also known as a variable frequency motor, is an electric motor designed to operate with an inverter drive or variable frequency drive (VFD).
Which type of inverter is used to control electric motors?
They are used in a number of applications both in industry and everyday life. There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as AC drives, variable speed drives (VSD), and variable frequency drives (VFD).
How do AC motor inverters work?
AC motor inverters utilize pulse width modulation (PWM) to create a variable voltage and frequency. In PWM, the inverter switches the power on and off rapidly, simulating an effective voltage. This method allows the inverter to control the required output efficiently. AC motor inverters also include feedback systems that monitor motor performance.
How do inverters control motor speed?
Frequency control: Inverters adjust the frequency of the output AC signal, which directly controls the speed of the motor. The principle of frequency-to-speed relationship indicates that increasing frequency increases motor speed.
What are the different types of inverter drives?
Following are some important types of inverter drives being utilised in the market today: AC VFDs: These drives are designed to control the speed and torque of three phase AC induction motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the electrical supply.
More related information
-
 How big a motor can a 250kw inverter power
How big a motor can a 250kw inverter power
-
 Medium and high power AC motor inverter
Medium and high power AC motor inverter
-
 Large water pump inverter solar power
Large water pump inverter solar power
-
 Three-phase photovoltaic inverter output power
Three-phase photovoltaic inverter output power
-
 Bhutan photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Bhutan photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
-
 160kw high power inverter
160kw high power inverter
-
 Can a 12v inverter power household electricity
Can a 12v inverter power household electricity
-
 30kw inverter for US off-grid photovoltaic power station
30kw inverter for US off-grid photovoltaic power station
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

