FEMA P-1019 Emergency Power Systems for Critical
This document examines the vulnerability of electrical power systems to natural hazards, describes what equipment in critical facilities should be supplied by emergency
Get Price
Job Safety Analysis and Activity Hazard Analysis for
When working with electrical power as part of our job, it is critical to use a job safety analysis or activity hazard analysis for electrical work to ensure proper
Get Price
Power Plant Construction Projects Risk Assessment: A Proposed
With the proposed method, which has been tested in real industrial facilities, it has been possible to increase the safety of the system and reduce the likelihood of incidents and
Get Price
Final+ +telecommunications | PDF | Base Station
A typical cellular telecommunication network consists of a number of base stations. Each base station is designed to serve a geographical area of network coverage and may be
Get Price
Optimum sizing and configuration of electrical system for
Typically, an electrical system of telecommunication base station consists of power sources such as grid power, solar power and generator power [4]. Fig. 1 illustrates a block
Get Price
Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution Industry
Describes five cases (six electrocutions) that resulted from the hazards of operating cranes near overhead power lines and makes recommendations for preventing similar incidents.
Get Price
Power Plant Construction Projects Risk Assessment:
With the proposed method, which has been tested in real industrial facilities, it has been possible to increase the safety of the system
Get Price
Power plant safety
Power plants are much safer than they once were; however, plant employees still encounter hazards. Training, along with proper operation and maintenance procedures, are
Get Price
Power station risk assessment
Process safety is very important on power stations due to hazards such as: fires or explosions following loss of fuel, explosions in high pressure steam
Get Price
Power Supply Safety Standards and Precautions | Bravo Electro
Electrical Shock: High-voltage power supplies generate dangerous current levels that can cause serious injury or death. Direct contact with live terminals, faulty wiring, or
Get Price
The 7 Best Portable Power Stations of 2025
Bring big backup power with you with these expert-recommended portable power stations, which can store enough power to charge electronics,
Get Price
Risk Factors of the Power Supply
Natural hazards include extreme weather, earthquakes, fire, epidemics/pandemics, and extraterrestrial hazards, while anthropogenic hazards include
Get Price
Ensure Safe Electrical Systems: Risk Assessments Guide
By systematically identifying hazards, analyzing their causes, and implementing targeted prevention and mitigation measures, these assessments safeguard personnel, equipment, and
Get Price
HAZARD IDENTIFICATION & RISK ASSESSMENT (HIRA)
Introduction Hazard analysis involves the identification and quantification of the various hazards (unsafe conditions) that exist in the project site. In this chapter, an attempt has been made
Get Price
Ensure Safe Electrical Systems: Risk Assessments
By systematically identifying hazards, analyzing their causes, and implementing targeted prevention and mitigation measures, these assessments safeguard
Get Price
Identification Hazards and Risk Assessment in Power Plant
During this process, there are several hazards associated with it such as exposure to coal dust, noise, vibration, heat stress entanglement between conveyors; so as to avoid these hazards,
Get Price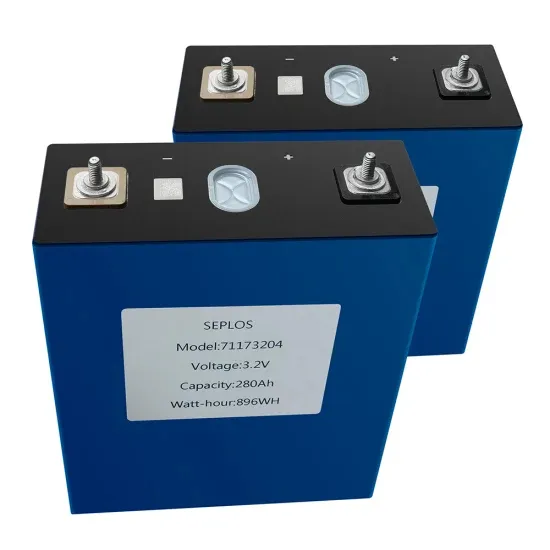
Power station risk assessment
Process safety is very important on power stations due to hazards such as: fires or explosions following loss of fuel, explosions in high pressure steam equipment, catastrophic rupture of
Get Price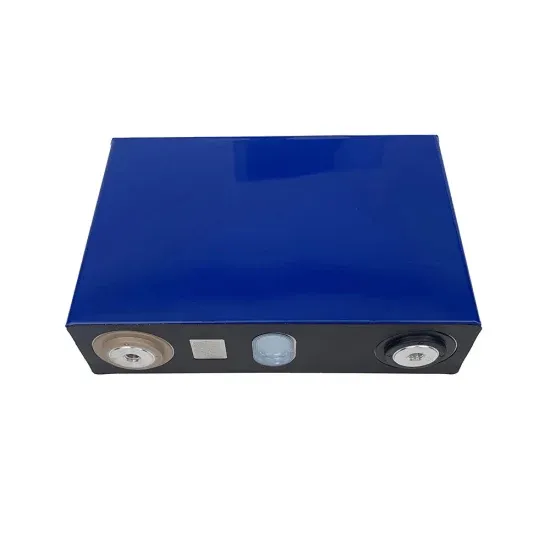
What Are the Risks Associated with Power Stations?
Power stations, while essential for energy generation, pose significant risks to workers and the surrounding environment. Key hazards include electrical shocks, chemical
Get Price
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY EM 385-1-1 U.S. Army Corps
> For complex or high hazard projects, the SSHO shall have a minimum of ten (10) years of safety-related work with at least five (5) years experience on similar type projects.
Get Price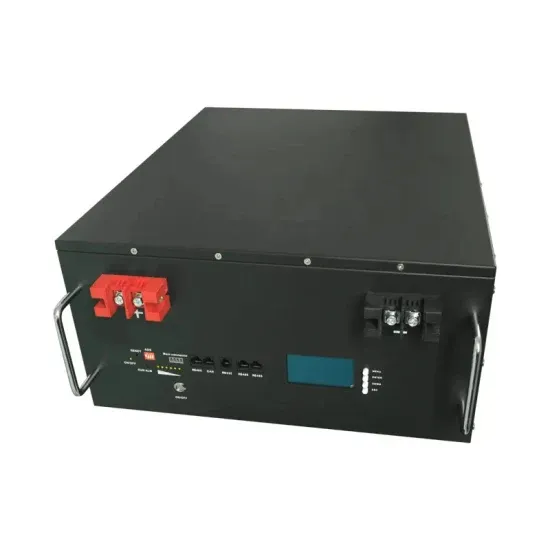
Paper62 420..424
This paper will describe how a hazard identification and assessment methodology developed within the chemical sector has been applied to operational Power Stations.
Get Price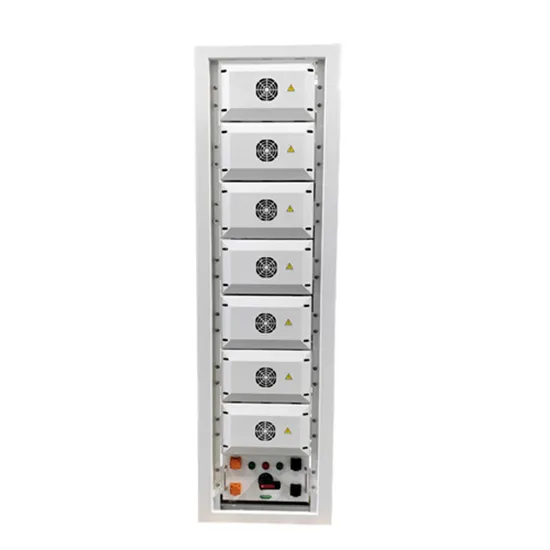
Power Supply Safety Standards and Precautions
Electrical Shock: High-voltage power supplies generate dangerous current levels that can cause serious injury or death. Direct contact with live
Get Price
Power Resilience: Guide for Water and Wastewater Utilities
Power loss can have devastating impacts on drinking water and wastewater utilities and the communities they serve. Inoperable pumps at a drinking water utility can make firefighting
Get Price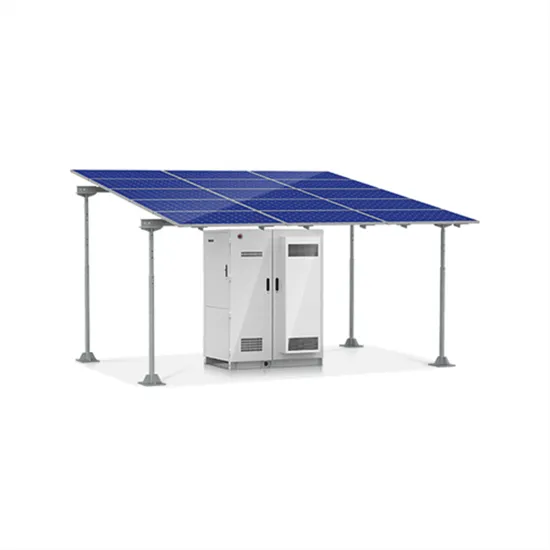
POWER GENERATION PLANT SAFETY GUIDE
POWER GENERATION PLANT SAFETY GUIDE Top Hazards in a Power Generation Plant Electrocution — Nearly 75% of all electrical work injuries are caused by arc flashes Boiler fire
Get Price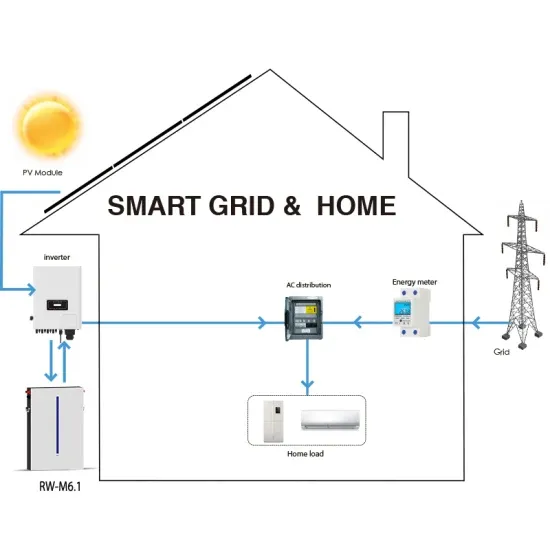
Power Plant Hazards
Hierarchy of Controls for Power Plant Hazards Elimination – Physically removing the hazard – this is the most effective hazard control. Consider moving a
Get Price
How to protect 5G macro base station amplifiers and antennas
This article describes macro base stations in detail and provides recommendations for protecting base station circuits, tower amplifiers and advanced antenna systems from sources of
Get Price
Risk Factors of the Power Supply
The hazard potential for critical infrastructures can be differentiated according to its focus on natural hazards and anthropogenic hazards. Natural hazards include extreme
Get Price
Renewable Energy Sources for Power Supply of Base Station Sites
An overview of research activity in the area of powering base station sites by means of renewable energy sources is given. It is shown that mobile network operators express significant interest
Get Price
Territory of Guam
This Energy Risk Profile examines the relative magnitude of the risks that the Territory of Guam''s energy infrastructure routinely encounters in comparison with the probable impacts. Natural
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Hazard sources in base station power supply projects]
What causes a process safety hazard in a power station?
Many power stations are being operated beyond their orig-inal design life increasing the risk of a process safety acci-dent due to the following factors. No hazard analysis during the design phase or records not available to the operating team. Process safety information incomplete, missing or out-of-date.
Why is a power supply a hazard?
This increases the risk of short circuits and electrical shock. Leakage Current: This refers to unintended current flow through the insulation or external parts of a power supply. It can pose a shock hazard, especially when sensitive equipment or personnel are involved.
What is a power plant risk assessment?
To make recommendations to mitigate the risk and hazards involved in the power plant. The goal of each risk assessment is to identify hazards, determine risk ranking with controls, and to revise the implementation of risk controls from the previous risk assessment sessions.
Does risk analysis improve safety in power plants?
The identification of hazards and risk assessment are key factors in the safety of the industries, including power plants. This paper contains an original risk analysis method that increases the level of safety in commissioning and start-up operations.
What are the power supply safety standards?
We’ll highlight the power supply safety standards below. At their most basic level, power supplies can be classified as one of three main categories based on their electrical insulation and grounding requirements. These are: Class I: Basic insulation and rely on grounding for safety.
Are you aware of power supply safety precautions?
You’re also aware of the safety concerns dealing with power supplies so you can protect yourself and others during installation, operation, maintenance, and replacement. Don’t overlook the power supply safety precautions we shared above.
More related information
-
 Uninterrupted power supply for Nepal base station room
Uninterrupted power supply for Nepal base station room
-
 Tajikistan 5G base station power supply and distribution facilities
Tajikistan 5G base station power supply and distribution facilities
-
 Vaduz 5G base station power supply changed
Vaduz 5G base station power supply changed
-
 What power supply does the base station outdoor cabinet provide
What power supply does the base station outdoor cabinet provide
-
 Base station wind power supply and wind power generation module
Base station wind power supply and wind power generation module
-
 Are there batteries in the power supply room of the telecom base station
Are there batteries in the power supply room of the telecom base station
-
 What is the difference between base station power supply and ordinary power supply
What is the difference between base station power supply and ordinary power supply
-
 Cambodia 5G base station power supply time
Cambodia 5G base station power supply time
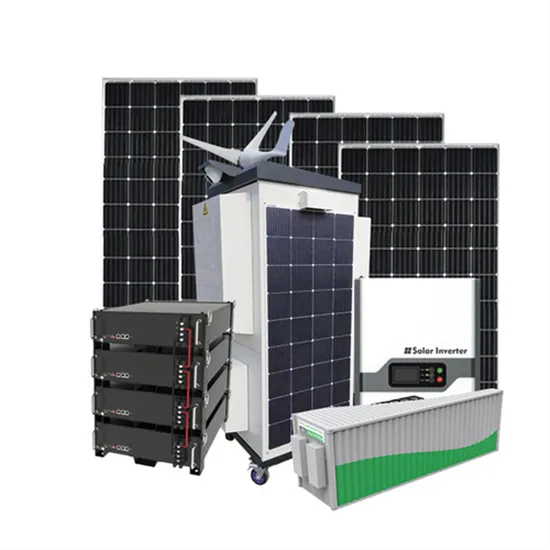
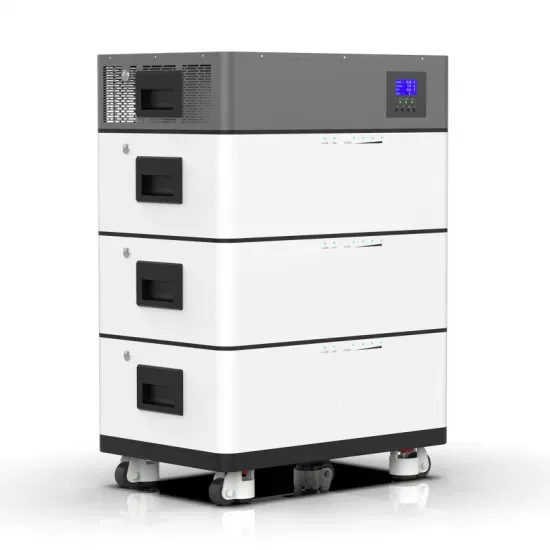
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


