Grid-scale batteries: They''re not just lithium
Zinc-bromine batteries Redflow has been manufacturing zinc-bromine flow batteries since 2010, Higgins said. These batteries do not require the critical minerals that
Get Price
5 Key Differences Between Flow Batteries and Lithium Ion Batteries
This article outlines these key differences between flow batteries and lithium ion ones so that you can make an informed decision regarding your next battery energy storage
Get Price
Comparative Analysis: Flow Battery vs Lithium Ion
Flow batteries are generally considered safer than lithium-ion batteries. The risk of thermal runaway is low, and they are less prone to
Get Price
Can Flow Batteries compete with Li-ion?
Like Li-ion batteries, within and between each category, flow batteries have different chemistries, including the most commonly used vanadium, and less frequently used zinc-bromine,
Get Price
Semi-solid flow battery
A schematic illustration of a typical semi-solid flow battery design [1] A semi-solid flow battery is a type of flow battery using solid battery active materials or involving solid species in the energy
Get Price
How do flow batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries
Flow batteries and lithium-ion batteries differ significantly in scalability and flexibility, with distinct advantages for different applications:
Get Price
What Is A Flow Battery? Overview Of Its Role In Grid-Scale
A flow battery is a type of rechargeable battery. It stores energy using electroactive species in liquid electrolytes. These electrolytes are stored in external tanks and pumped
Get Price
Coupling redox flow desalination with lithium recovery from spent
Here, we demonstrate a redox flow system to couple redox flow desalination with lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries. The spontaneous reaction between a battery
Get Price
Revolutionary Liquid Flow Battery Is Better Than Any Current Li-Ion
Typically, they involve two chemical liquids that flow over the opposite sides of an ion-exchange membrane to create a flow of electric current. Their energy density is usually
Get Price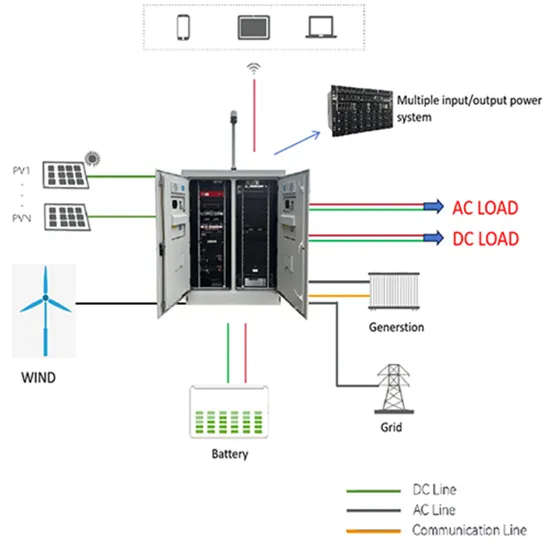
Lithium-Ion Batteries vs Flow Batteries: Which One Fits Your
In this article we will discuss the comparison of lithium-ion batteries vs flow batteries, starting from the definition, advantages and disadvantages of these two batteries, to tips on choosing a
Get Price
What are solid-state batteries and why do we need
The lithium-ion batteries that we rely on in our phones, laptops and electric cars have a liquid electrolyte, through which ions flow in one direction
Get Price
How Lithium Batteries Work: A Beginner''s Guide
This seamless exchange of ions and electrons, along with lightweight and high-capacity materials, is what enables lithium-ion batteries to
Get Price
How Do Flow Batteries Compare to Lithium-Ion for Grid Storage?
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and faster response times but degrade faster (10-15 years) and face thermal risks. Flow batteries use liquid electrolytes,
Get Price
Influit develops liquid lithium ion flow batteries
The flow battery design passes anolyte and catholyte liquids past each other on either side of an ion exchange membrane to generate current. The system needs four tanks, for spent and
Get Price
(PDF) Comparative analysis of lithium-ion and flow batteries for
Flow batteries have a competitive advantage in terms of cycle life, providing a longer duration of 1000 cycles compared to Lithium-ion batteries, which only offer 500 cycles.
Get Price
Advancing Flow Batteries: High Energy Density and
This innovative battery addresses the limitations of traditional lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and Zn-air batteries, contributing advanced
Get Price
Comparative analysis of lithium-ion and flow batteries for
In addition, Lithium-ion batteries demonstrate superior charging capabilities of 50 kW and discharging rates of 70 kW, surpassing Flow batteries which have charging rates of 30 kW and
Get Price
nanoFlowcell
In contrast to lead batteries or lithium-ion batteries, redox flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes. The electrolyte liquids for flow cells are usually
Get Price
Can Flow Batteries Finally Beat Lithium?
Flow batteries are safe, stable, long-lasting, and easily refilled, qualities that suit them well for balancing the grid, providing uninterrupted power, and backing up sources of
Get Price
Revolutionary Liquid Flow Battery Is Better Than Any
Typically, they involve two chemical liquids that flow over the opposite sides of an ion-exchange membrane to create a flow of electric
Get Price
Comparative Analysis: Flow Battery vs Lithium Ion
Flow and lithium-ion batteries are promising energy storage solutions with unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
Get Price
Comparative Analysis: Flow Battery vs Lithium Ion
Flow batteries are generally considered safer than lithium-ion batteries. The risk of thermal runaway is low, and they are less prone to catching fire or exploding.
Get Price
Comparing Lithium-ion and Flow Batteries for Solar Energy Storage
This significant difference arises from the design and chemistry of the batteries; lithium-ion batteries degrade over time due to electrode wear and electrolyte decomposition,
Get Price
How do flow batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries in terms of
Flow batteries and lithium-ion batteries differ significantly in scalability and flexibility, with distinct advantages for different applications: Energy storage can be increased
Get Price
Inexpensive New Liquid Battery Could Replace $10,000 Lithium
3 days ago· How flow batteries work Dr Cara Doherty, a study co-author from the CSIRO, said flow batteries store energy in liquids rather than solid materials like those found in lithium-ion
Get Price
5 Key Differences Between Flow Batteries and Lithium
The differences between flow batteries and lithium ion batteries are cost, longevity, power density, safety and space efficiency.
Get Price
How lithium dendrites form in liquid batteries | Science
In flow batteries (12), accelerated ion transport in the bulk electrolyte leads to the deposition of Li metal with much larger particle sizes (lower surface area).
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Are lithium-ion batteries liquid flow batteries]
What is the difference between flow and lithium ion batteries?
Both flow and lithium ion batteries provide renewable energy storage solutions. Both types of battery technology offer more efficient demand management with lower peak electrical demand and lower utility charges. Key differences between flow batteries and lithium ion ones include cost, longevity, power density, safety and space efficiency.
Are flow batteries safer than lithium ion batteries?
Flow batteries are generally considered safer than lithium-ion batteries. The risk of thermal runaway is low, and they are less prone to catching fire or exploding. Lithium-ion Batteries Lithium-ion batteries ‘ safety is a significant concern due to their susceptibility to thermal runaway, which can lead to fires or explosions.
What is a liquid flow battery?
A liquid flow battery is a type of energy storage system that rely on fluids, called nanoelectrofuels (NEF), to generate electricity. They have been researched for many years and typically involve two chemical liquids that flow over the opposite sides of an ion-exchange membrane to create a flow of electric current. Unlike Li-Ion batteries, they do not rely on solid electrodes.
Are liquid flow batteries better than Li-ion batteries?
Liquid flow batteries, such as those with a 23% higher energy density than the best Li-Ion batteries, are more efficient in generating electricity. They rely on fluids, called nanoelectrofuels (NEF), instead of the solid electrodes used in Li-Ion batteries. Liquid flow batteries have been researched for many years.
What are lithium ion batteries?
Lithium ion batteries is a leading rechargeable battery storage technology with a relatively short lifespan (when compared to flow batteries). Their design involves only one encased battery cell in which electrolytes mix with conductors to charge and discharge.
How does the Influit liquid flow battery function?
The Influit liquid flow battery functions with four nozzles in the dispensers, one for each tank, allowing for simultaneous draining of spent fuels and refilling of fresh ones. Impressively, it has a higher energy density by volume than lithium-ion batteries, with approximately 23% more energy – around 350-550 Wh/l at the system level for the Gen1 battery.
More related information
-
 Cost per kilowatt-hour of electricity from all-vanadium liquid flow batteries
Cost per kilowatt-hour of electricity from all-vanadium liquid flow batteries
-
 Recommendations for liquid flow batteries for solar base stations in the Republic of Congo
Recommendations for liquid flow batteries for solar base stations in the Republic of Congo
-
 What are the advantages of all-vanadium liquid flow batteries
What are the advantages of all-vanadium liquid flow batteries
-
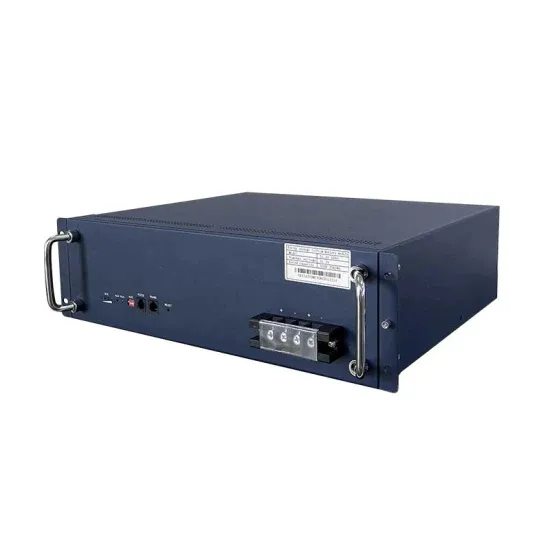 Liquid flow battery
Liquid flow battery
-
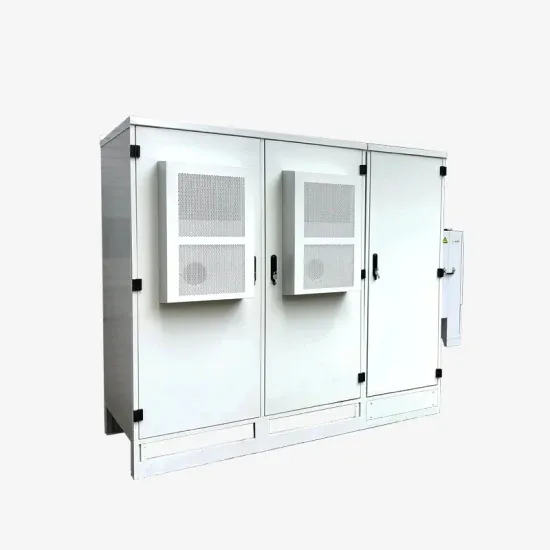 Swiss All-Vanadium Liquid Flow Energy Storage Project
Swiss All-Vanadium Liquid Flow Energy Storage Project
-
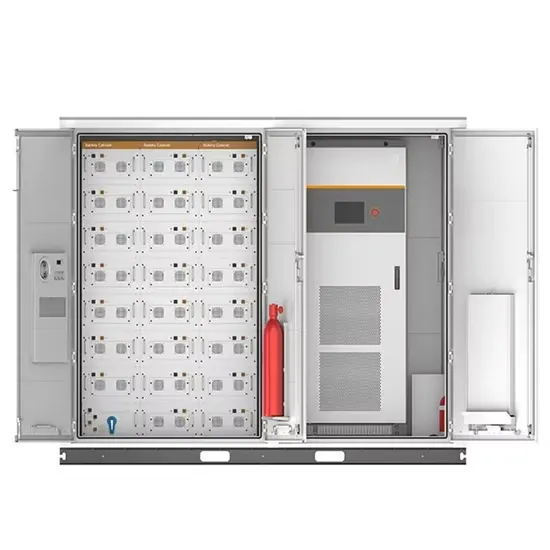 Palau all-vanadium liquid flow energy storage power station
Palau all-vanadium liquid flow energy storage power station
-
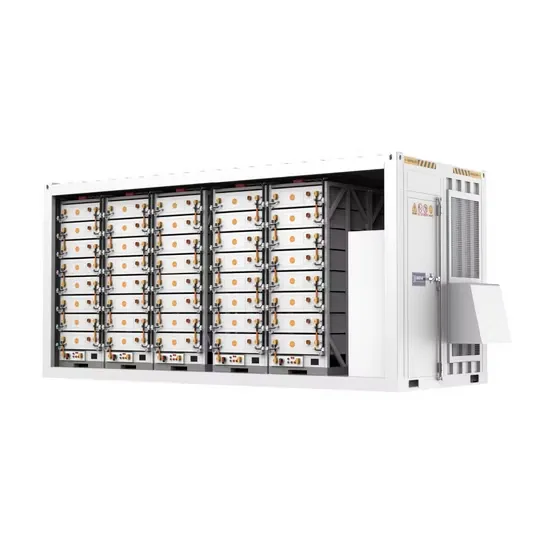 Spain s new all-vanadium liquid flow energy storage cabinet
Spain s new all-vanadium liquid flow energy storage cabinet
-
 How many communication base station flow batteries are there in Burundi
How many communication base station flow batteries are there in Burundi
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


