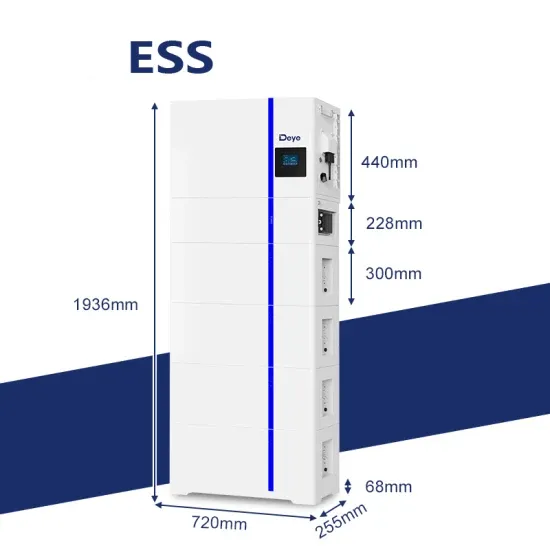
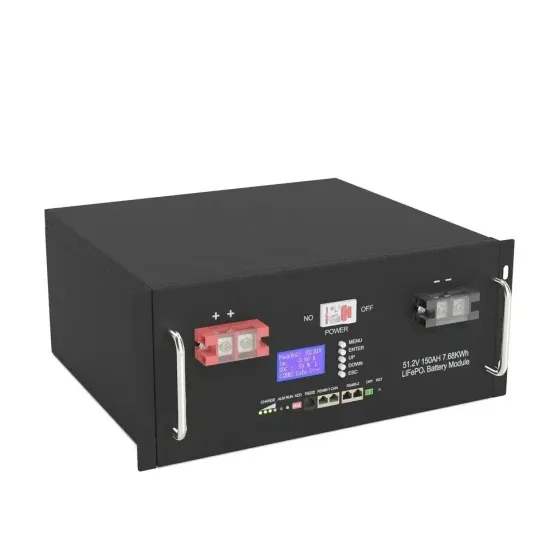
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC voltage in manufacturing.
Get Price
Power Converters (AC-DC, DC-AC, DC-DC & AC-AC)
Need to convert AC to DC, DC to AC, or something else? We explore 4 essential power converters: rectifiers, inverters, buck/boost
Get Price
EcoFlow US | Converter vs Inverter
Unlike inverters, which change Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), converters typically transform the voltage level but maintain the same current.
Get Price
(PDF) Current Source Inverter (CSI) Power
Grid converters play a central role in renewable energy conversion. Among all inverter topologies, the current source inverter (CSI)
Get Price
Inverter vs. Converter: What''s the Difference, Which
A converter can convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or vice versa. On the other hand, an inverter converts direct current (DC) into
Get Price
Power Conversion | Yaskawa Global Site
The power conversion technology, which controls the voltage, current, and frequency of the input power supply to convert it to the intended output, has
Get Price
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses, How It
An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household
Get Price
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from electronic components called diodes,
Get Price
Converter vs Inverter
Converters and inverters are electrical devices that convert current. Converters convert the voltage of an electric device, usually alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). On the
Get Price
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get Price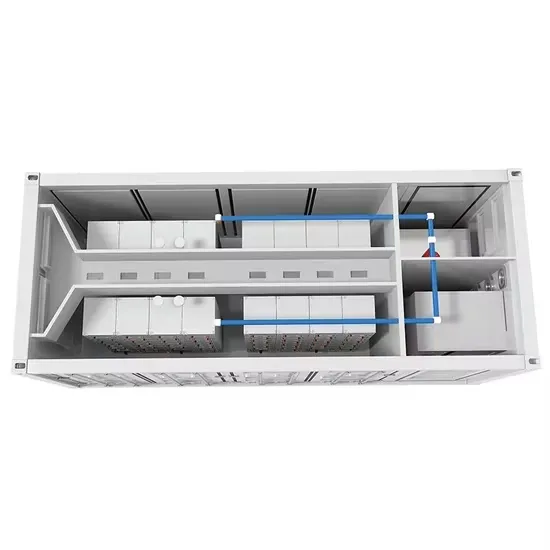
How does the power conversion system (PCS) or hybrid inverter
A Power Conversion System (PCS), often called a hybrid inverter in a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), is a key component that manages the flow of electrical
Get Price
Inverters and converters
In the narrow sense, the term "inverter" refers to a circuit (function) that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). However, in Japan, many
Get Price
Inverter AC to DC Amperage Conversion Calculator | Battery Stuff
Our calculator will help you determine the DC amperage as it passes through a power inverter and provides the wattage rating you are pulling so you can properly size the
Get Price
Difference Between Inverter and Converter –
An inverter is primarily used to convert DC to AC, while a converter adjusts voltage levels or changes the type of current from AC to DC
Get Price
Inverters Vs. Converters | What''s The Difference?
An inverter converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current), whereas a converter modifies voltage and current within the same current type (AC to DC, DC to DC, or AC to AC).
Get Price
Measurement of the Conversion Efficiency of High
Evaluating the power conversion efficiency of high-voltage solar inverters requires current sensors and power analyzers capable of accommodating DC voltages
Get Price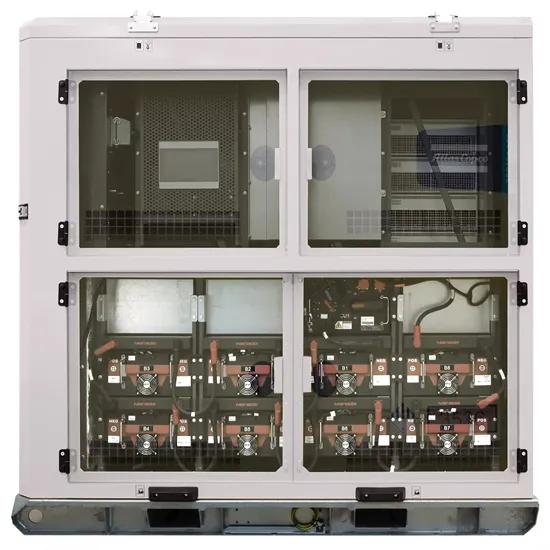
Difference Between Inverter and Converter – Explained Clearly
An inverter is primarily used to convert DC to AC, while a converter adjusts voltage levels or changes the type of current from AC to DC or vice versa. When selecting a
Get Price
Current Source Inverter (CSI) Power Converters in
Grid converters play a central role in renewable energy conversion. Among all inverter topologies, the current source inverter (CSI)
Get Price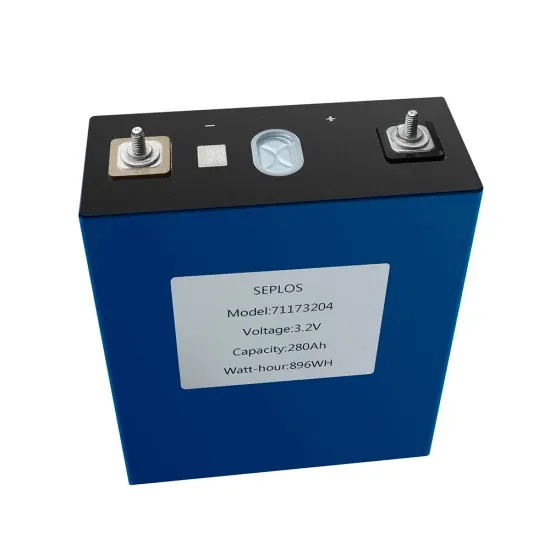
What is an inverter? | inverter
An inverter or power inverter, refers to an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). In our daily life, we often convert 110V or 220V AC
Get Price
Understanding Power Converters : A Beginners Guide
What is a Power Converter? A power converter is a device or an electronic circuit that converts electrical energy from one form to another, adapting it to the needs of various
Get Price
Voltage converter
A common use of the voltage converter is for a device that allows appliances made for the mains voltage of one geographical region to operate in an area with different voltage. Such a device
Get Price
EcoFlow US | Converter vs Inverter
A converter is an electrical device that modifies the form of an electrical power source. Its primary function is to convert voltage, either stepping it up
Get Price
What to Know about DC to AC Voltage Conversion?
Learn everything you need to know about DC to AC voltage conversion, including why it''s necessary, how it works, the role of inverters, and common applications like solar
Get Price
Inverters and converters
In the narrow sense, the term "inverter" refers to a circuit (function) that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). However, in Japan, many people think of an inverter as a
Get Price
Inverter vs converter: What''s the difference?
Converters change the voltage of an electrical power source and can convert AC to DC (rectification) or DC to AC (inversion). Inverters specifically convert DC into AC.
Get Price
Inverter vs. Converter: What''s the Difference, Which Do You
A converter can convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or vice versa. On the other hand, an inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
Get Price
How to Use a Voltage Converter? | inverter
Voltage converters, which are a category of transformers, are what we often call household transformers, indicating that it is suitable for home use. It is also called a power
Get Price
Inverter Vs Transformer: Key Differences, Pros, And
No DC-to-AC Conversion Unlike inverters, transformers don''t convert DC to AC, making them ideal for AC-to-AC voltage conversion in systems that already
Get Price
Converter vs Inverter
An inverter converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current), whereas a converter modifies voltage and current within the same current type (AC to
Get Price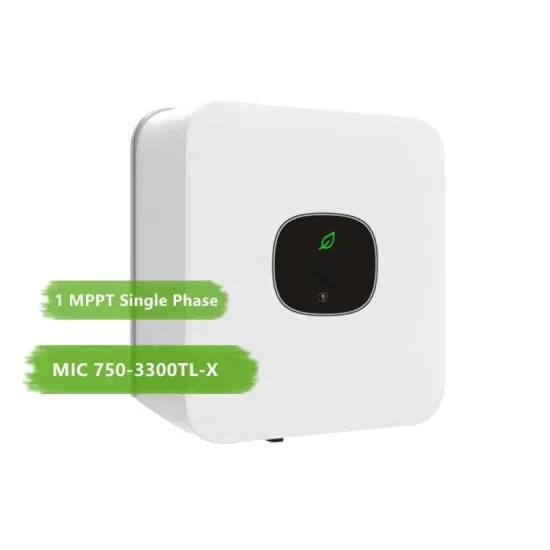
6 FAQs about [Inverter current conversion voltage conversion]
What is the difference between an inverter and a converter?
An inverter converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current), whereas a converter modifies voltage and current within the same current type (AC to DC, DC to DC, or AC to AC). Inverters are commonly used in renewable energy systems, while converters regulate power supply in electronic devices. 2. Can an inverter work without a battery?
How does an inverter convert DC to AC?
An inverter converts Direct Current (DC) to Alternating Current (AC) electricity (and vice-versa). It plays a critical role in on-grid and solar power. Electricity is transmitted over power lines and also stored in batteries as DC. For most consumer applications, an inverter must convert the DC into AC (household) electricity.
What is the difference between AC converter and DC inverter?
Below are the main differences: Functionality Inverters: Convert DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current). Converters: Convert either AC to DC (rectification) or adjust the DC voltage from one level to another (DC-DC conversion). They can also change AC voltages (AC to AC converters). Applications
What is a DC inverter?
An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It is widely used in applications where AC power is required but only a DC source is available, such as in solar energy systems and battery-powered devices. 4.2. How Inverters Convert DC to AC
What is a converter circuit & inverter circuit?
An inverter is composed of the front part and the rear part. The front part, the “converter circuit” converts AC to DC while the rear part, the “inverter circuit” converts DC to AC. From a broad perspective, the converter circuit and inverter circuit are used as a set to perform AC to AC conversion.
How does a DC inverter work?
Electricity is transmitted over power lines and also stored in batteries as DC. For most consumer applications, an inverter must convert the DC into AC (household) electricity. Inside an inverter, a complex electronic circuit rapidly alternates DC power back and forth, emulating the AC power waveform.
More related information
-
 What is the appropriate current and voltage of the inverter
What is the appropriate current and voltage of the inverter
-
 String inverter current and voltage
String inverter current and voltage
-
 Can increasing the voltage of the inverter increase the current
Can increasing the voltage of the inverter increase the current
-
 What is the inverter voltage and current
What is the inverter voltage and current
-
 VFD inverter neutral point voltage
VFD inverter neutral point voltage
-
 Inverter output voltage through
Inverter output voltage through
-
 Two-stage inverter front-stage DC voltage
Two-stage inverter front-stage DC voltage
-
 Three-phase constant voltage variable frequency inverter
Three-phase constant voltage variable frequency inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


