Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low
Get Price
Harmonics and Inverters
With PWM inverters, the output impedance stays very low up to high frequencies and the output voltage distortion due to circulating currents, even highly distorted currents, can be neglected.
Get Price
The role and difference between high voltage inverter
High-voltage inverters are typically used in industry for high-power, high-voltage (usually over 1kV) applications. They can provide high
Get Price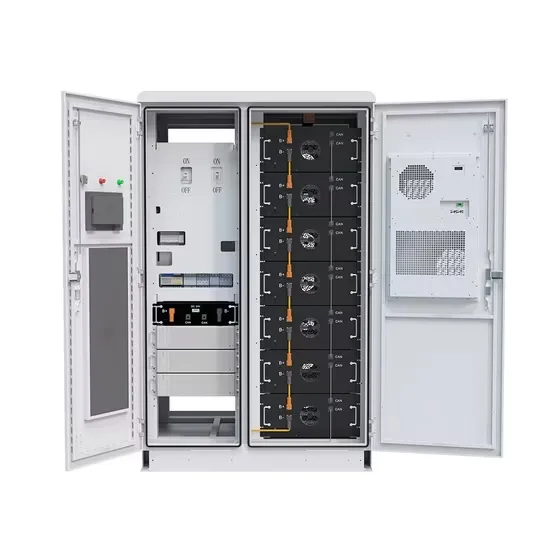
Inverter too high output voltage than normal, problem?
Hi, One of the inverter of my school generating peak AC voltage of around 280V. My country''s standard mains voltage is around 220 to 230V AC. I have noticed that some cell
Get Price
power supply
Low voltage and high current means you need to spend more on copper/cables. Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable
Get Price
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
You''ll learn what high-voltage and low-voltage inverters do, how they work, and where each type is best used. We''ll also talk about the benefits and drawbacks of each, along
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get Price
Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and
The choice between a low-voltage inverter and a high-voltage inverter often depends on specific application requirements, including the scale of the operation, efficiency concerns, and safety
Get Price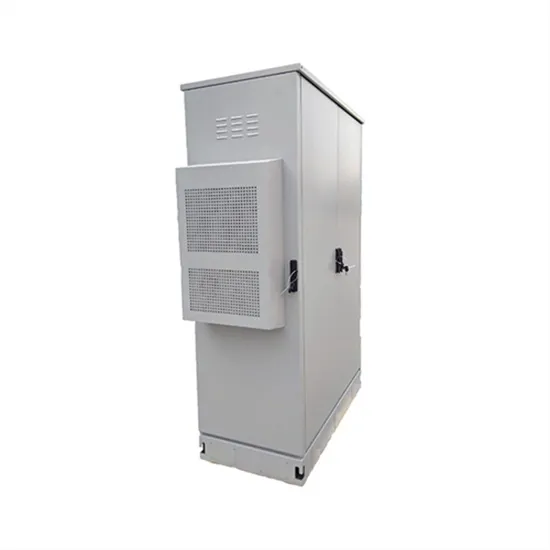
The role and difference between high voltage inverter and low voltage
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low-power applications in homes and
Get Price
Inverters, Types and Voltages
Browse our recommended inverters for every type of setup—from low voltage off-grid systems to high voltage, grid-tied solutions. Each product is reviewed to ensure it meets
Get Price
The current status and development of DC/AC inverter
The traditional DC/AC inverter technology of the low-frequency link inverter process has been gradually replaced by the high-frequency band
Get Price
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
What is the Purpose of an Inverter Drive? The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to
Get Price
Inverting Regulators | Analog Devices
Analog Devices'' line of dc-to-dc invertering switching regulators is specifically designed to invert input voltages to negative outputs. It offers input voltage
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get Price
Spikes in CMOS Inverter transients
The discussion centers on the sharp voltage spikes observed in a CMOS inverter simulation using CADENCE, particularly during transitions from low to high and high to low
Get Price
The difference between high-voltage inverter and low-voltage
This article briefly introduces the difference between high-voltage inverter and low-voltage inverter in terms of operating voltage range, application scenarios, advantages and disadvantages,
Get Price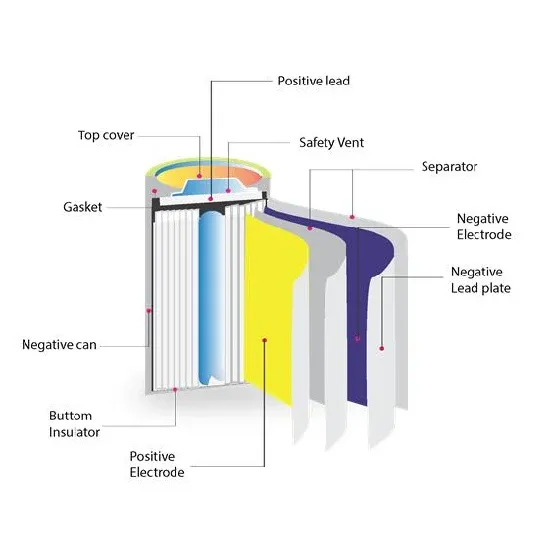
How to Troubleshoot and Fix Common Inverter Problems
Here are some steps to follow: Check the input voltage. The input voltage to the inverter should be within the specified range. If the input voltage is too low or
Get Price
Power Inverters: The Need-to-Know Essentials
Inverters used in applications with high currents and voltage are known as power inverters. Inverters used in applications with low currents and voltages are known as
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
Inverter Current Formula: Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the load, the
Get Price
Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and high
The choice between a low-voltage inverter and a high-voltage inverter often depends on specific application requirements, including the scale of the operation, efficiency concerns, and safety
Get Price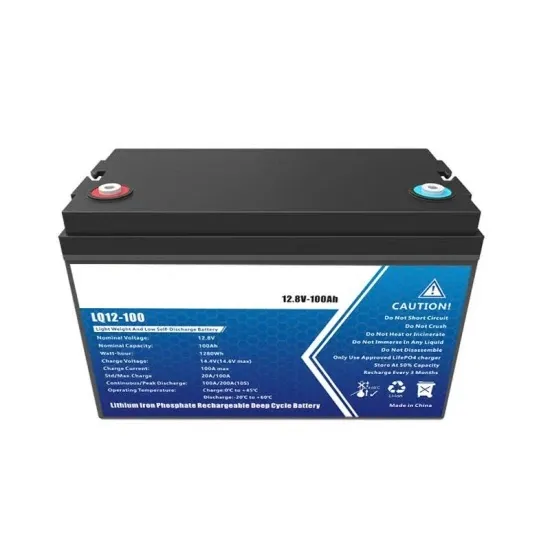
The difference between high-voltage inverter and low-voltage inverter
This article briefly introduces the difference between high-voltage inverter and low-voltage inverter in terms of operating voltage range, application scenarios, advantages and disadvantages,
Get Price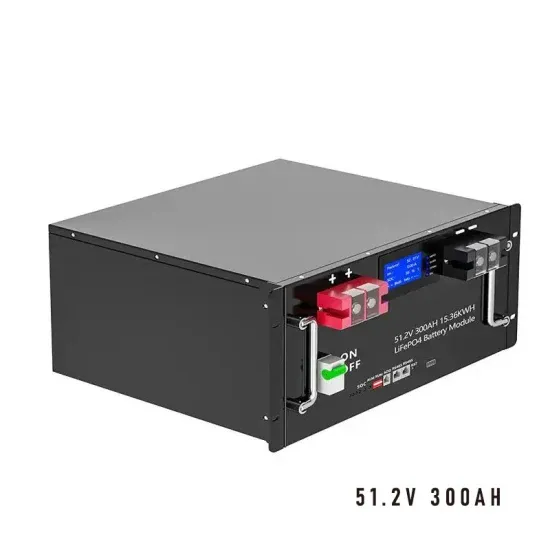
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
The article provides an overview of inverter in renewable energy systems, focusing on their role in converting DC to AC, their efficiency, and
Get Price
Inverter Transformer and its Working Principle
The inverters produce AC by switching the polarity of the DC power source, and almost all industries and residential areas need Alternating Current for usage. Inverters are of
Get Price
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
The inverter can be defined as the device which converts DC input supply into AC output where input may be a voltage source or current source. Inverters are mainly classified into two main
Get Price
Lecture 19: Inverters, Part 3
Lecture 19 - Inverters 3 Prof. David Perreault We have seen that we can use harmonic elimination to eliminate low-frequency harmonic content at the expense of high switching frequency (with
Get Price
High Voltage Inverters: Understanding Its Benefits and Applications
Explore high voltage inverters, their benefits, applications, and how to protect them for optimal performance.
Get Price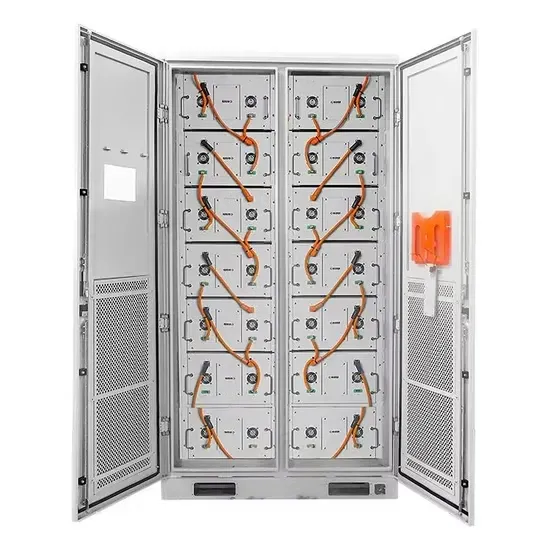
More related information
-
 Inverter high current voltage becomes low
Inverter high current voltage becomes low
-
 Weak current to high voltage inverter
Weak current to high voltage inverter
-
 Is the communication base station inverter high voltage or low voltage
Is the communication base station inverter high voltage or low voltage
-
 Australian low voltage inverter manufacturer
Australian low voltage inverter manufacturer
-
 What is a new energy high voltage inverter
What is a new energy high voltage inverter
-
 Photovoltaic low voltage to medium voltage inverter
Photovoltaic low voltage to medium voltage inverter
-
 10kV high voltage inverter
10kV high voltage inverter
-
 Inverter pv 1 voltage is low
Inverter pv 1 voltage is low
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


